static const struct spi_eeprom_device_t eeprom_devices[] = {
{ "25X010", 128, 1, 0, 0, 8, 10000 }, //8 and 16 byte page varients
//{ "25X010", 128, 1, 0, 0, 16 },//use the lowest common page size
{ "25X020", 256, 1, 0, 0, 8, 10000 },
//{ "25X020", 256, 1, 0, 0, 16 },
{ "25X040", 512, 1, 1, 3, 8, 10000 },
//{ "25X040", 512, 1, 1, 3, 16 },
{ "25X080", 1024, 2, 0, 0, 16, 10000 },
//{ "25X080", 1024, 2, 0, 0, 32 },
{ "25X160", 2048, 2, 0, 0, 16, 10000 },
//{ "25X160", 2048, 2, 0, 0, 32 },
{ "25X320", 4096, 2, 0, 0, 32, 10000 },
{ "25X640", 8192, 2, 0, 0, 32, 10000 },
{ "25X128", 16384, 2, 0, 0, 64, 10000 },
{ "25X256", 32768, 2, 0, 0, 64, 10000 },
{ "25X512", 65536, 2, 0, 0, 128, 10000 },
{ "25XM01", 131072, 3, 0, 0, 256, 10000 },
{ "25XM02", 262144, 3, 0, 0, 256, 5000 }, //5MHz
{ "25XM04", 524288, 3, 0, 0, 256, 8000 }
};
I narrowed the list of SPI EEPROMs down to this set with common page sizes and addressing methods.
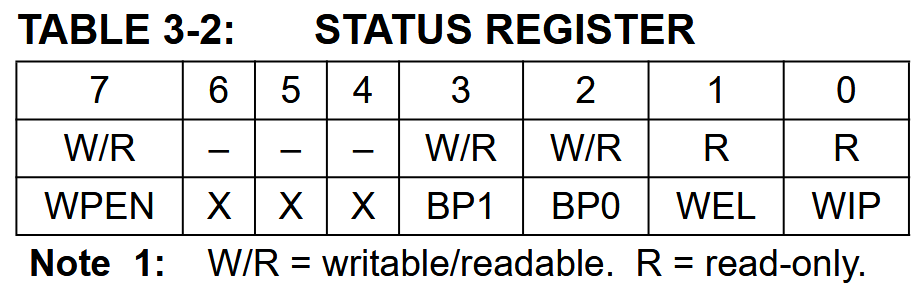
The status register bit 0 indicates a write is in progress, bit 1 indicates if the write enable latch is set (data can be written to the memory or status register).
Write protection blocks
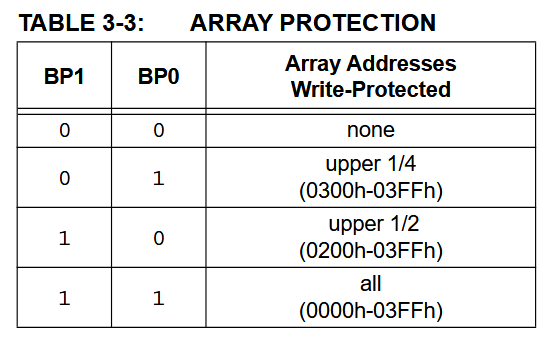
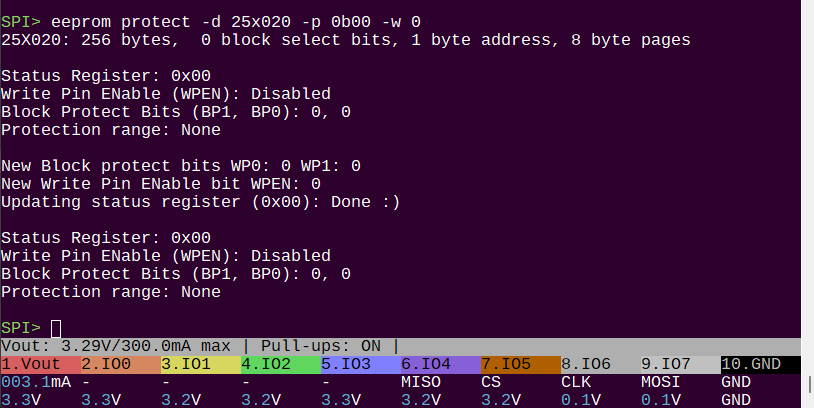
Many, but not all, EEPROMs have a write block protection feature. This allows you to protect a portion of the EEPROM from being written to, even if the write enable latch is set. The block select bits are used to select which block is protected: none (0b00), the upper 1/4 (0b01), the upper 1/2 (0b10), or the entire EEPROM (0b11).
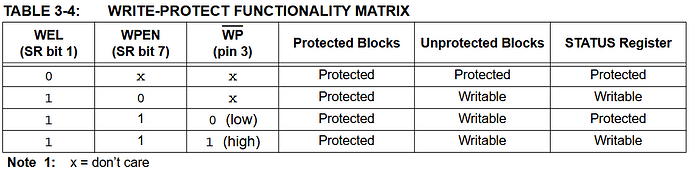
Fewer devices have a WPEN bit that disables the Write Protect (WP) pin. When WPEN is 0, the WP pin is ignored. When WPEN is 1, the WP pin is used to control write protection. If the WP pin is high, the EEPROM is write protected. If the WP pin is low, the EEPROM can be written to.
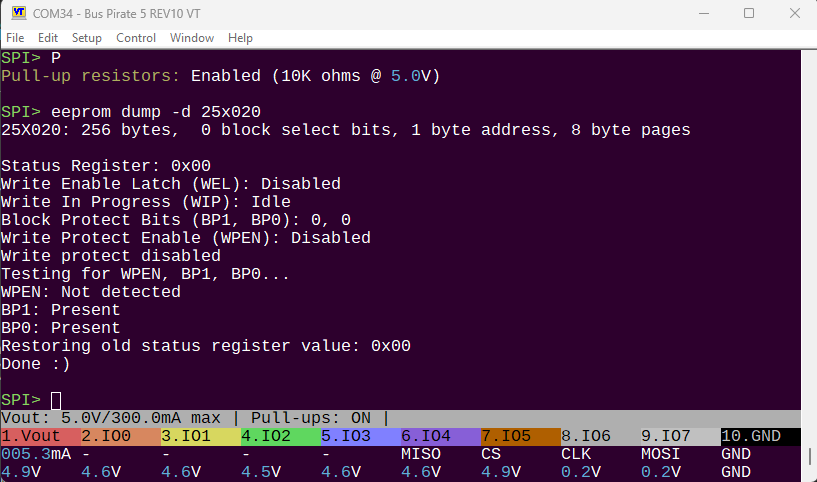
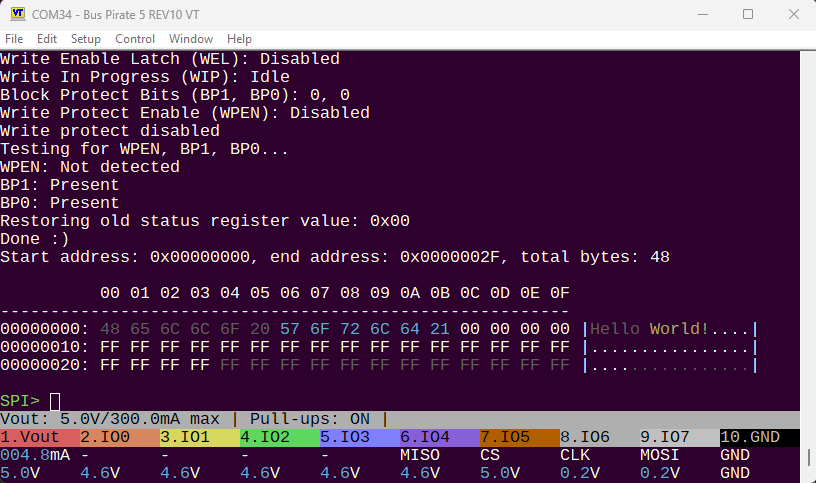
We can test which bits are available in a chip by writing 0b10001100 to the status register, enabling all the protection bits. If the chip supports WPEN or BPx bits, they will be set to 1 after the write. If they are not supported, they will remain 0. This chip has BPx bits, but not WPEN bit.
ETA: dump working, with new greyed out regions not requested by the user: